Colang 核心概念#
本指南建立在 Hello World 指南 的基础上,介绍了您在开始使用 NeMo Guardrails 时应理解的核心 Colang 概念。
先决条件#
这个 “Hello World” Guardrails 配置使用了 OpenAI gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct 模型。
安装
openai包
pip install openai
设置
OPENAI_API_KEY环境变量
export OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY # Replace with your own key
如果您在 notebook 中运行此代码,请修补 AsyncIO 循环。
import nest_asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
什么是 Colang?#
Colang 是一种用于对话式应用程序的建模语言。使用 Colang 可以设计用户与 bot 之间的对话流程。
注意
在本指南中,bot 指的是整个基于 LLM 的对话式应用程序。
核心概念#
在 Colang 中,两个核心概念是 messages(消息)和 flows(流程)。
消息(Messages)#
在 Colang 中,对话被建模为用户和 bot 之间的消息交换。一条交换的消息有一个 utterance(话语),例如 “你能做什么?”,以及一个 canonical form(规范形式),例如 ask about capabilities。规范形式是将话语转述为标准、通常更短的形式。
使用 Colang,您可以定义对您的基于 LLM 的应用程序很重要的用户消息。例如,在 “Hello World” 示例中,express greeting 用户消息被定义为
define user express greeting
"Hello"
"Hi"
"Wassup?"
express greeting 表示规范形式,而 “Hello”、“Hi” 和 “Wassup?” 表示示例话语。示例话语的作用是教导 bot 已定义规范形式的含义。
您还可以定义 bot 消息,例如 bot 应如何与用户对话。例如,在 “Hello World” 示例中,express greeting 和 ask how are you bot 消息被定义为
define bot express greeting
"Hey there!"
define bot ask how are you
"How are you doing?"
如果为同一规范形式提供了多个话语,则 bot 在使用该消息时会随机选择一个话语。
如果您想知道 用户消息规范形式 是否与经典意图相同,答案是肯定的。您可以将它们视为意图。但是,在使用它们时,bot 不受限于仅使用预定义的列表。
流程(Flows)#
在 Colang 中,flows 表示用户和 bot 之间的交互模式。最简单的形式是用户和 bot 消息的序列。在 “Hello World” 示例中,greeting flow 被定义为
define flow greeting
user express greeting
bot express greeting
bot ask how are you
这个 flow 指示 bot 在每次用户打招呼时,回应问候语并询问用户的感受。
Guardrails#
消息和 flows 为定义 guardrails(或简称 rails)提供了核心构建块。前面的 greeting flow 实际上是一个 rail,它指导 LLM 如何回应问候语。
工作原理#
本节回答以下问题
如何使用用户和 bot 消息定义?
如何提示 LLM 以及进行了多少次调用?
我可以使用没有示例话语的 bot 消息吗?
我们以下面的问候语为例。
from nemoguardrails import RailsConfig, LLMRails
config = RailsConfig.from_path("./config")
rails = LLMRails(config)
response = rails.generate(messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello!"
}])
print(response["content"])
Hello World!
How are you doing?
ExplainInfo 类#
要获取有关 LLM 调用的信息,请调用 LLMRails 类的 explain 函数。
# Fetch the `ExplainInfo` object.
info = rails.explain()
Colang 历史#
使用 colang_history 函数以 Colang 格式检索对话历史。这向我们展示了确切的消息及其规范形式
print(info.colang_history)
user "Hello!"
express greeting
bot express greeting
"Hello World!"
bot ask how are you
"How are you doing?"
LLM 调用#
使用 print_llm_calls_summary 函数列出已进行的 LLM 调用摘要
info.print_llm_calls_summary()
Summary: 1 LLM call(s) took 0.48 seconds and used 524 tokens.
1. Task `generate_user_intent` took 0.48 seconds and used 524 tokens.
info 对象还包含一个 info.llm_calls 属性,其中包含每个 LLM 调用的详细信息。该属性将在后续指南中进行描述。
过程#
一旦从用户接收到输入消息,多步过程便开始了。
步骤 1:计算用户消息的规范形式#
在从用户接收到话语(例如前面示例中的“Hello!”)后,Guardrails 实例使用 LLM 计算相应的规范形式。
注意
NeMo Guardrails 使用面向任务的交互模型与 LLM 进行交互。每次调用 LLM 时,它都会使用特定的任务 prompt 模板,例如 generate_user_intent、generate_next_step、generate_bot_message。详细信息请参见默认模板 prompt。
在处理 “Hello!” 消息的情况下,使用 generate_user_intent 任务 prompt 模板进行一次 LLM 调用。该 prompt 如下所示
print(info.llm_calls[0].prompt)
"""
Below is a conversation between a helpful AI assistant and a user. The bot is designed to generate human-like text based on the input that it receives. The bot is talkative and provides lots of specific details. If the bot does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.
"""
# This is how a conversation between a user and the bot can go:
user "Hello there!"
express greeting
bot express greeting
"Hello! How can I assist you today?"
user "What can you do for me?"
ask about capabilities
bot respond about capabilities
"As an AI assistant, I can help you with a wide range of tasks. This includes question answering on various topics, generating text for various purposes and providing suggestions based on your preferences."
user "Tell me a bit about the history of NVIDIA."
ask general question
bot response for general question
"NVIDIA is a technology company that specializes in designing and manufacturing graphics processing units (GPUs) and other computer hardware. The company was founded in 1993 by Jen-Hsun Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem."
user "tell me more"
request more information
bot provide more information
"Initially, the company focused on developing 3D graphics processing technology for the PC gaming market. In 1999, NVIDIA released the GeForce 256, the world's first GPU, which was a major breakthrough for the gaming industry. The company continued to innovate in the GPU space, releasing new products and expanding into other markets such as professional graphics, mobile devices, and artificial intelligence."
user "thanks"
express appreciation
bot express appreciation and offer additional help
"You're welcome. If you have any more questions or if there's anything else I can help you with, please don't hesitate to ask."
# This is how the user talks:
user "Wassup?"
express greeting
user "Hi"
express greeting
user "Hello"
express greeting
# This is the current conversation between the user and the bot:
# Choose intent from this list: express greeting
user "Hello there!"
express greeting
bot express greeting
"Hello! How can I assist you today?"
user "What can you do for me?"
ask about capabilities
bot respond about capabilities
"As an AI assistant, I can help you with a wide range of tasks. This includes question answering on various topics, generating text for various purposes and providing suggestions based on your preferences."
user "Hello!"
该 prompt 包含四个逻辑部分
一组通用指令。这些指令可以使用 config.yml 中的
instructions键进行配置。一个示例对话,也可以使用 config.yml 中的
sample_conversation键进行配置。一组用于将用户话语转换为规范形式的示例。通过对所有用户消息示例执行向量搜索来选择最相关的五个示例。更多详细信息请参见ABC Bot。
当前对话,前面是示例对话的前两个轮次。
对于 generate_user_intent 任务,LLM 必须预测最后一个用户话语的规范形式。
print(info.llm_calls[0].completion)
express greeting
正如我们所见,LLM 正确预测了 express greeting 规范形式。它甚至进一步预测了 bot 应该做什么,即 bot express greeting,以及应该使用的话语。然而,对于 generate_user_intent 任务,仅使用预测的第一行。如果您想让 LLM 在一次调用中预测所有内容,可以在 config.yml 中将 rails.dialog.single_call 键设置为 True 来启用单次 LLM 调用选项。
步骤 2:确定下一步#
计算出用户消息的规范形式后,Guardrails 实例需要决定接下来应该发生什么。有两种情况
如果存在与规范形式匹配的 flow,则使用该 flow。该 flow 可以决定 bot 应该回复特定消息,或执行某个 action。
如果没有 flow,则使用
generate_next_step任务提示 LLM 以获取下一步。
在我们的示例中,与 greeting flow 匹配,下一步是
bot express greeting
bot ask how are you
步骤 3:生成 bot 消息
步骤 3:生成 bot 消息#
一旦决定了 bot 应该说什么的规范形式,就必须生成消息。有两种情况
如果找到预定义的消息,则使用确切的话语。如果同一个规范形式关联了多个示例话语,则随机使用其中一个。
如果不存在预定义的消息,则使用 generate_bot_message 任务提示 LLM 生成消息。
在我们的 “Hello World” 示例中,使用了预定义的消息“Hello world!”和“How are you doing?”。
后续问题#
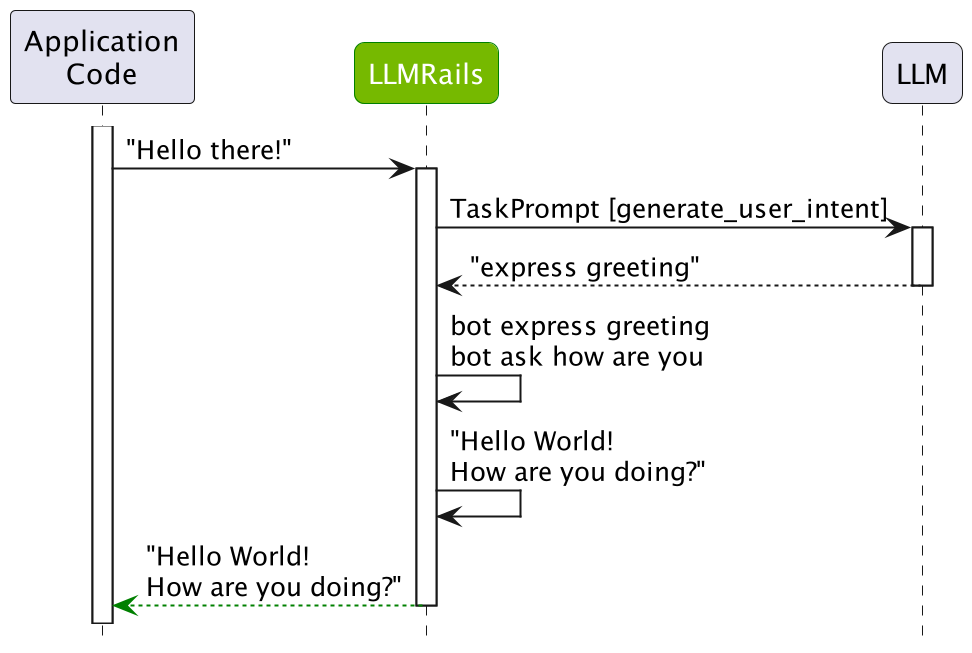
在前面的示例中,LLM 被提示一次。下图总结了上述步骤序列
response = rails.generate(messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is the capital of France?"
}])
print(response["content"])
The capital of France is Paris.
让我们对后续问题“法国的首都是哪里?”检查相同的过程。
info = rails.explain()
print(info.colang_history)
user "What is the capital of France?"
ask general question
bot response for general question
"The capital of France is Paris."
让我们检查 Colang 历史
info.print_llm_calls_summary()
Summary: 3 LLM call(s) took 1.79 seconds and used 1374 tokens.
1. Task `generate_user_intent` took 0.63 seconds and used 546 tokens.
2. Task `generate_next_steps` took 0.64 seconds and used 216 tokens.
3. Task `generate_bot_message` took 0.53 seconds and used 612 tokens.
以及 LLM 调用
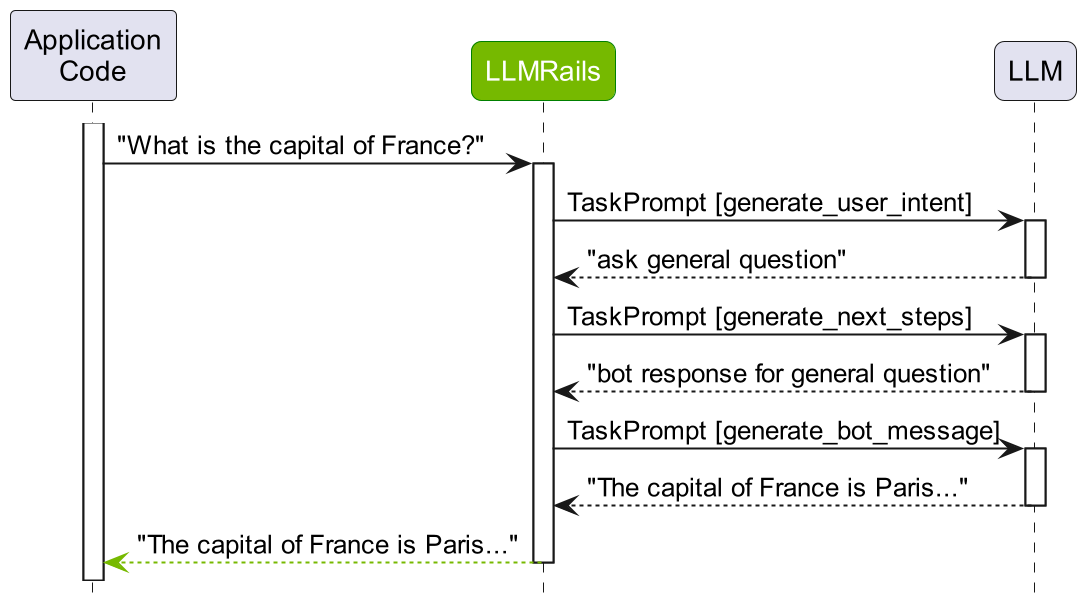
基于这些步骤,我们可以看到用户话语“法国的首都是哪里?”的规范形式被预测为 ask general question。由于没有与之匹配的 flow,LLM 被要求预测下一步,在这种情况下是 bot response for general question。此外,由于没有预定义的回复,LLM 第三次被要求预测最终消息。
总结#
本指南详细概述了两个核心 Colang 概念:messages(消息)和 flows(流程)。它还探讨了消息和 flow 定义在底层如何使用以及如何提示 LLM。更多详细信息,请参阅Python API 和 Colang 语言语法 的参考文档。
下一步#