Guardrails 流程#
本指南概述了 NeMo Guardrails 中支持的主要 rails 类型以及调用它们的过程。
概述#
NeMo Guardrails 支持五大类 rails:输入、对话、输出、检索和执行。下图概述了通过这些类别流程的高级流程。
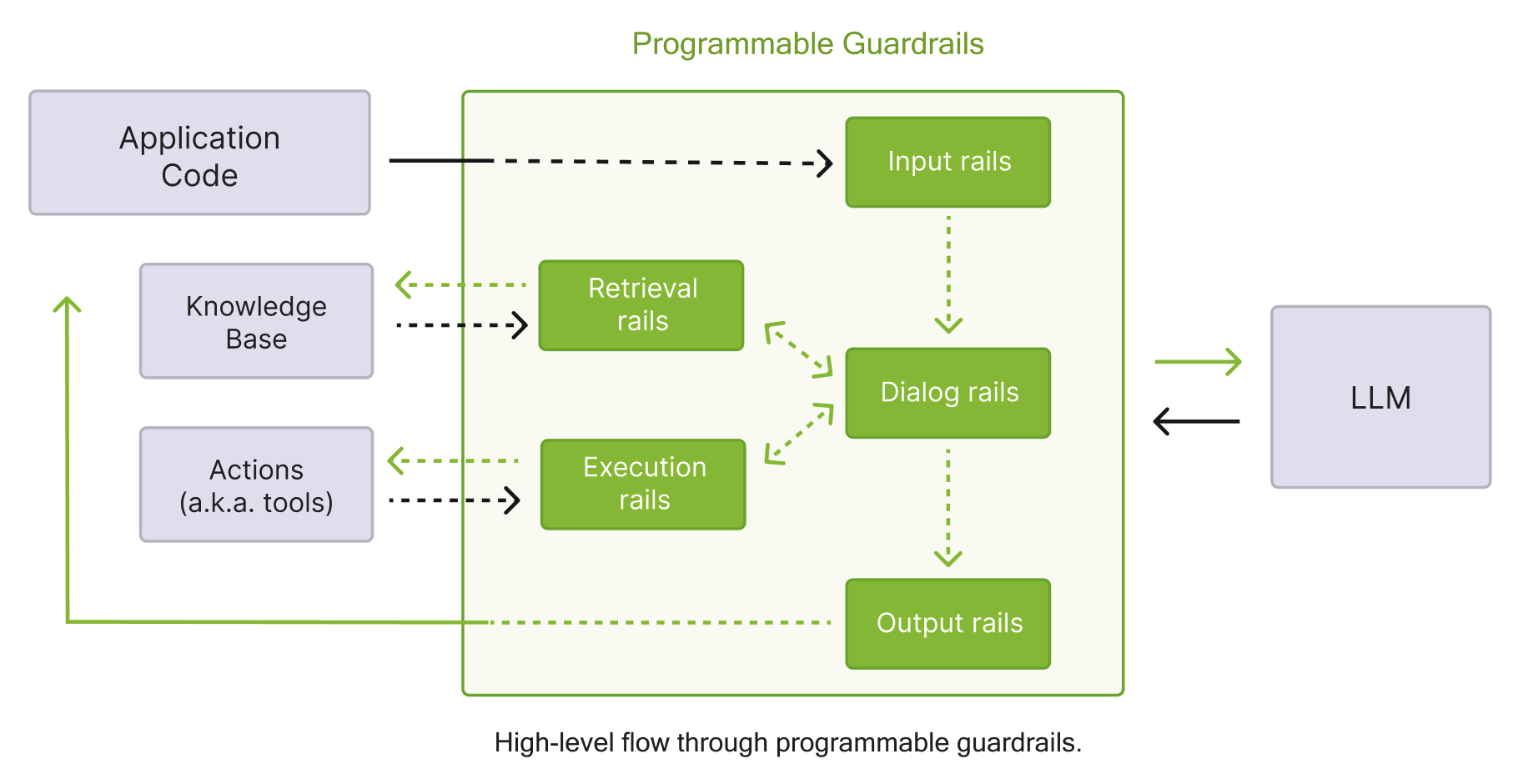
Rails 的类别#
NeMo Guardrails 中支持五种类型的 rails
输入 rails:应用于来自用户的输入;输入 rail 可以拒绝输入(停止任何其他处理)或更改输入(例如,屏蔽潜在的敏感数据,重新措辞)。
对话 rails:影响对话的演变方式以及 LLM 的提示方式;对话 rails 对规范形式消息进行操作(更多详情请参见此处),并确定是否应执行操作,是否应调用 LLM 以生成下一步或响应,是否应改用预定义的响应等。
检索 rails:应用于 RAG(检索增强生成)场景中检索到的块;检索 rail 可以拒绝块,阻止其用于提示 LLM,或更改相关块(例如,屏蔽潜在的敏感数据)。
执行 rails:应用于需要调用的自定义操作(也称为工具)的输入/输出。
输出 rails:应用于 LLM 生成的输出;输出 rail 可以拒绝输出,阻止将其返回给用户或更改它(例如,删除敏感数据)。
Guardrails 流程#
下图详细描述了 guardrails 流程
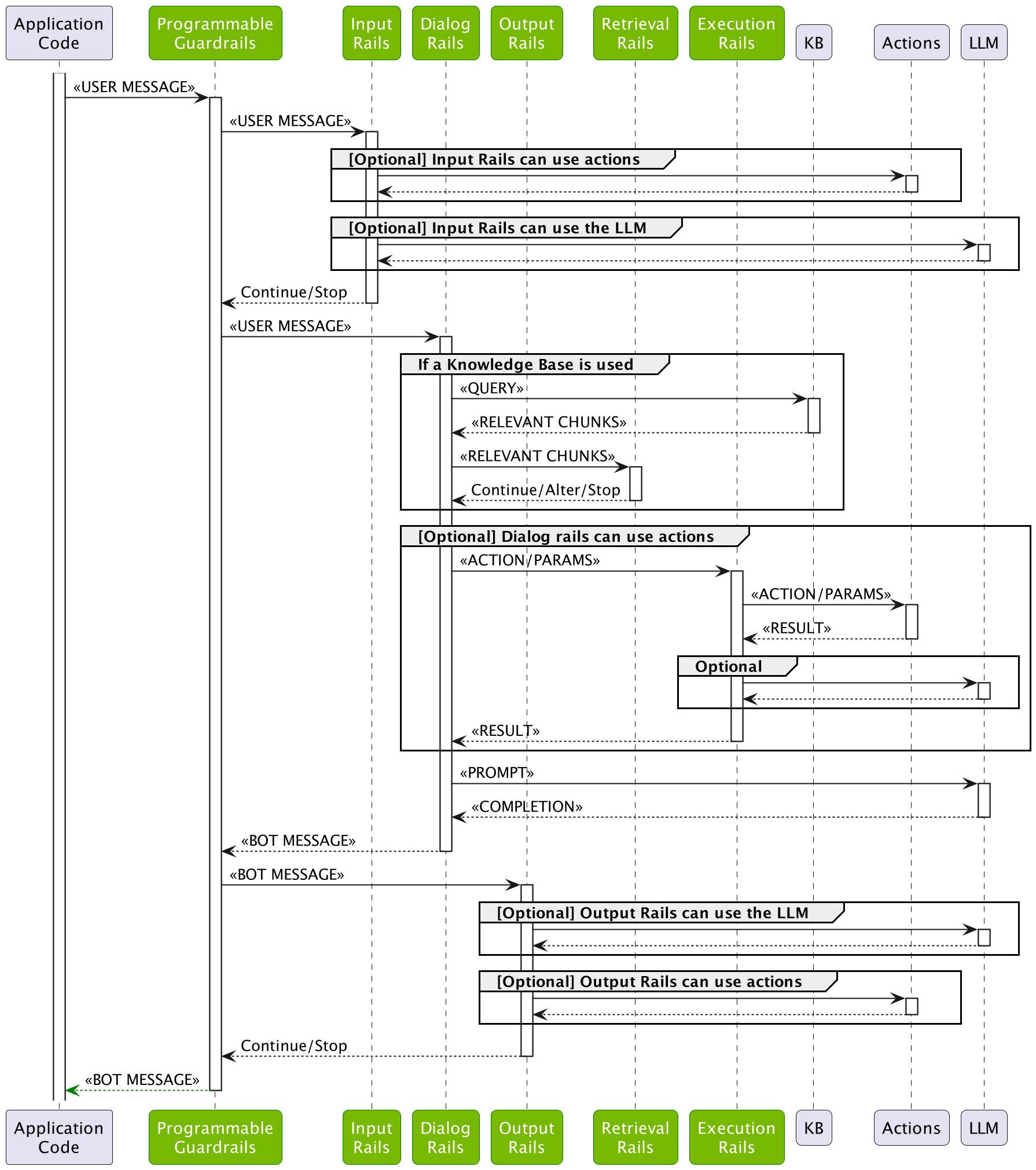
guardrails 流程包含用户消息要经历的多个阶段
输入验证阶段:用户输入首先由输入 rails 处理。输入 rails 决定是否允许输入,是否应更改或拒绝输入。
对话阶段:如果允许输入且配置包含对话 rails(即,至少定义了一条用户消息),则用户消息由对话 flows 处理。 这最终将产生一条 bot 消息。
输出验证阶段:在对话 rails 生成 bot 消息后,它会由输出 rails 处理。 输出 rails 决定是否允许输出,是否应更改或拒绝输出。
对话 Rails 流程#
下图详细描述了对话 rails 流程
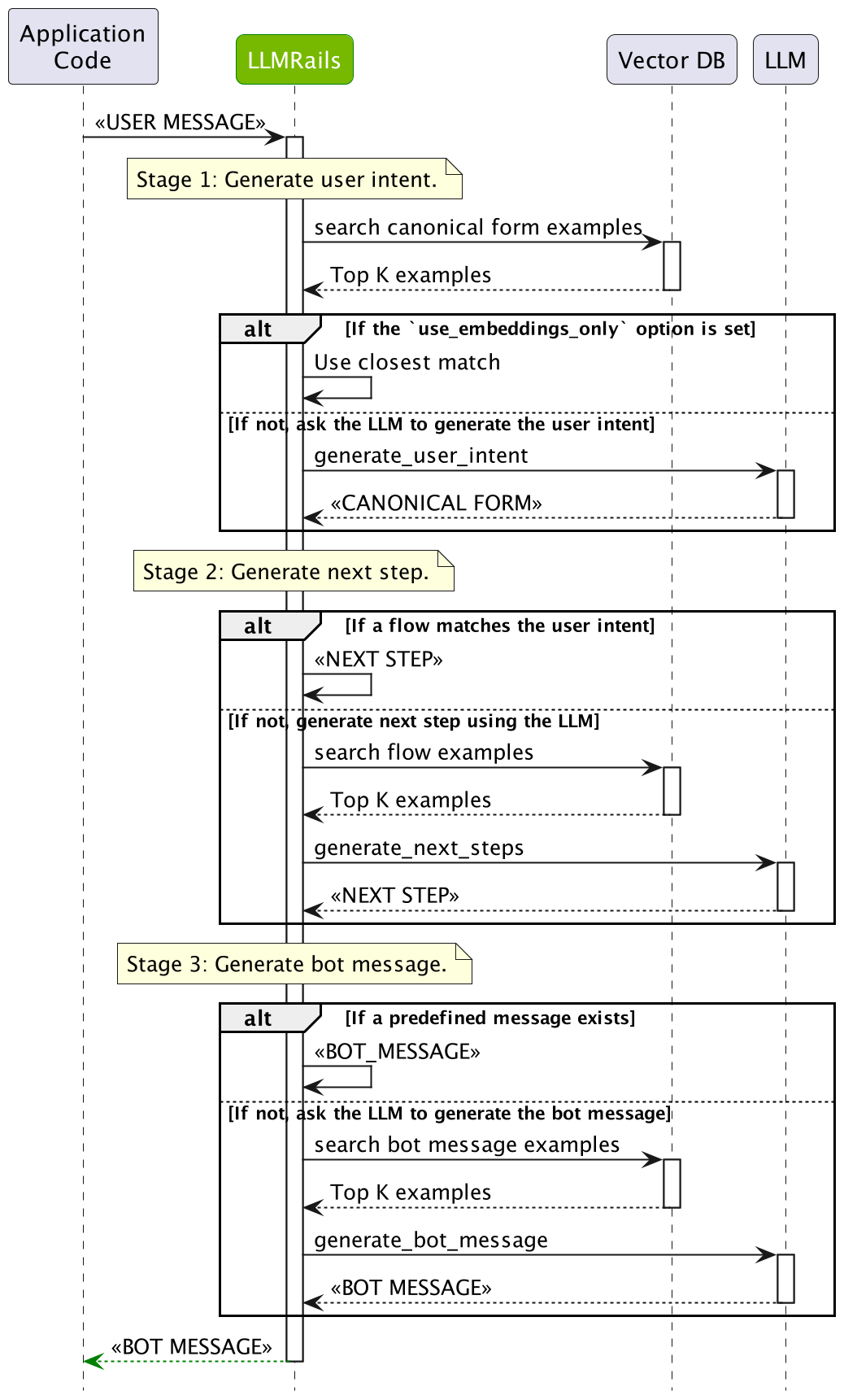
对话 rails 流程包含用户消息要经历的多个阶段
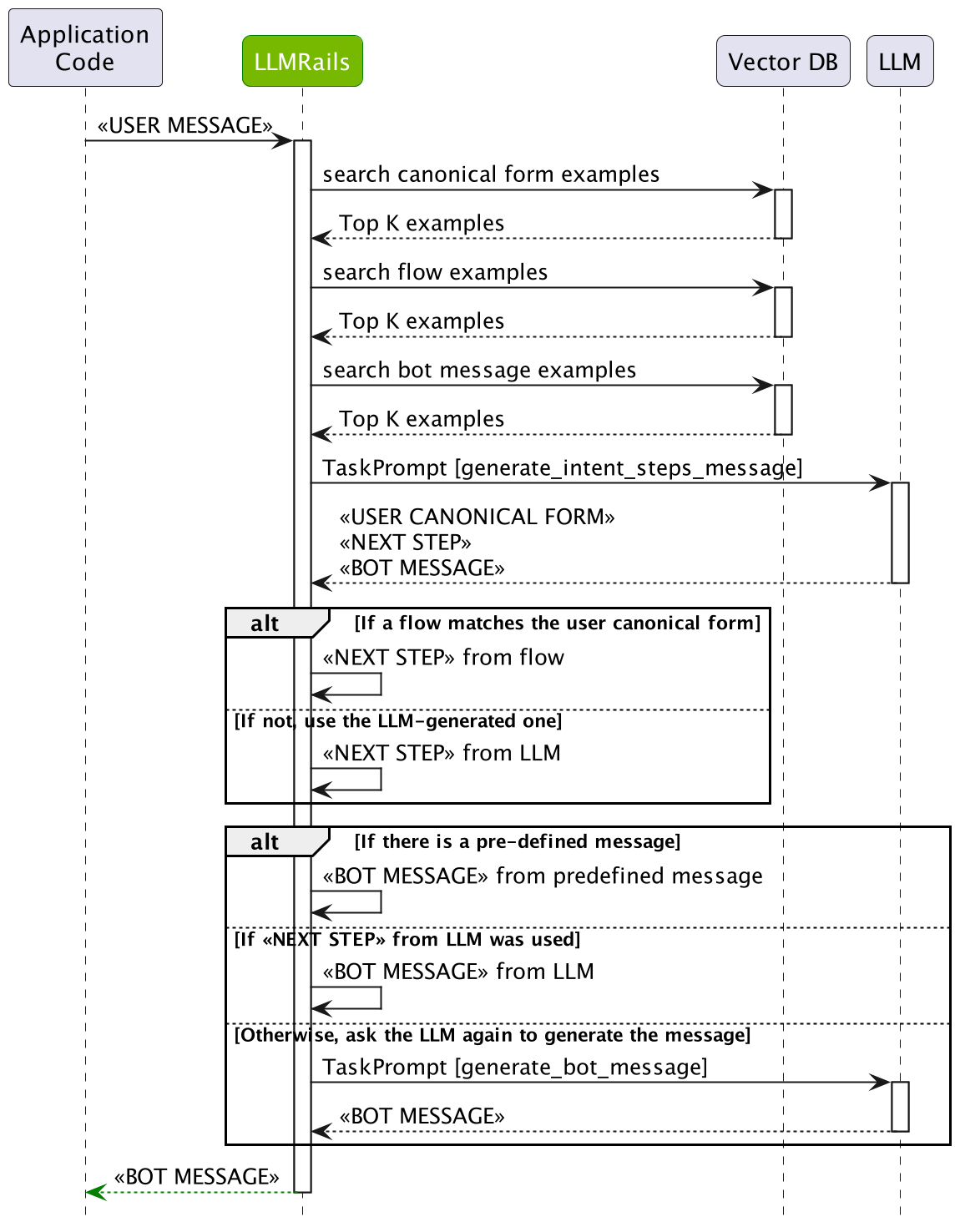
用户意图生成:首先,必须通过计算规范形式(也称为用户意图)来解释用户消息。 这是通过搜索来自已定义用户消息的最相似示例,然后要求 LLM 生成当前规范形式来完成的。
下一步预测:在计算出用户消息的规范形式后,需要预测下一步。 如果存在与规范形式匹配的 Colang flow,则将使用该 flow 来做出决定。 如果没有,则会要求 LLM 使用已定义 flow 中最相似的示例来生成下一步。
Bot 消息生成:最终,需要根据规范形式生成 bot 消息。 如果存在预定义消息,则将使用该消息。 如果没有,则会要求 LLM 使用最相似的示例来生成 bot 消息。
单次 LLM 调用#
当 single_llm_call.enabled 设置为 True 时,对话 rails 流程将简化为一次 LLM 调用,一次性预测所有步骤。下图描述了简化的对话 rails 流程